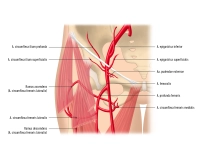
1. Femoral artery
1,1. Overview
| Origin |
|
| Course |
|
| Branches |
|
| Distribution |
|
1,2. Major branches of femoral artery
| Branches | Distribution | |
| Superficial epigastric artery |
|
|
| Superficial iliac circumflex artery |
|
|
| Deep femoral artery |
|
|
| External pudendal arteries |
|
|
| Descending genicular artery |
|
|
2. Popliteal artery
2,1. Overview
| Origin |
|
| Course |
|
| Branches |
|
| Distribution |
|
2,2. Major branches of popliteal artery
| Course | Branches | Distribution | |
| Anterior tibial artery |
|
|
|
From a surgical viewpoint, it is customary to divide the popliteal artery into three segments (P1–P3) which determine the surgical access routes:
Segment | Feature | Access |
P1 | From adductor hiatus to the top of the patella | Distal medial thigh |
P2 | From top of the patella to center of the knee joint | Posterior (popliteal fossa) |
P3 | From center of the knee joint to anterior tibial artery origin | Proximal medial lower leg |
The popliteal artery lies in a nerve-vascular (NV) bundle encased in fatty connective tissue. In segments P1 and P2, the artery is anteromedial to the popliteal vein, while in segment P3, it is surrounded by its accompanying veins. The tibial and common peroneal nerves lie posterolateral to the popliteal artery and vein. In the popliteal fossa, the nerves follow a rather superficial course, which must be taken into account when exposing the popliteal artery from the posterior aspect.
The superficial and deep lymphatic drainage is bundled in the popliteal fossa via three to five perivenous lymph nodes.
Due to its location, the popliteal artery is subjected to considerable mechanical loading, which is why, as a muscular-type artery, it has strong muscle and fiber layers (tunica media vasis, internal elastic membrane. Its mural characteristics thus resemble those of central elastic arteries.
3. Posterior tibial artery
3,1. Overview
| Origin | o Continuation of popliteal artery distal to origin of anterior tibial artery |
| Course | o Passes together with tibial nerve posterior to tendinous arch of soleus → Medial malleolar sulcus → Medial malleolus o Bifurcates into medial + lateral plantar artery |
| Branches | o Fibular artery o Medial + lateral plantar artery |
| Distribution | o Dorsal aspect of lower leg o Sole of foot |
3,2. Major branches of posterior tibial artery
| Course | Branches | Distribution | |
| Fibular artery | o Courses along dorsal aspect of fibula o Lies posterior tibial and flexor hallucis longus muscles | o Communicating branch: Cross-connection to posterior tibial artery o Lateral malleolar branches | o Lateroposterior lower leg |
| Medial plantar artery | o Courses in medial neurovascular bundle of sole of foot (medial plantar artery, vein and nerve) between abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis muscles | o Ø | o Medial sole of foot |
| Lateral plantar artery | o Courses in lateral neurovascular bundle of sole of foot (lateral plantar artery, vein and nerve) between flexor digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae muscles | o Deep plantar arch: anastomosis between lateral plantar artery and deep plantar branch of dorsalis pedis artery at the metatarsals | o Lateral sole of foot o Toes |