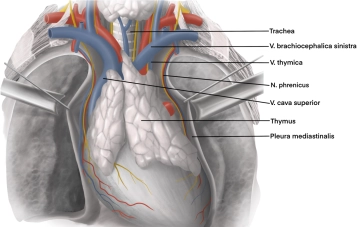
The thymus (also known as the breast gland) is a bilobed organ located ventrally in the upper mediastinum, immediately anterior to the confluence of the right and left brachiocephalic veins. Caudally, the thymus extends to the pericardium and is laterally bounded by the pleura's reflection margins. The space between both pleural sacs is also referred to as the thymic triangle.
The activity of the thymus (imprinting of the immune system, development, and differentiation of T-lymphocytes) stagnates upon entering puberty. In adults, the thymus consists only of minimally functional residual tissue surrounded by a well developed fat pad formed by involution, also known as the thymic remnant body.