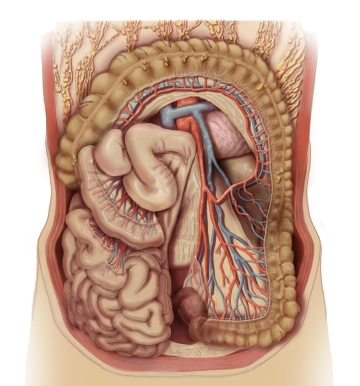
- Arterial supply of the left hemicolon, sigmoid colon up to the upper rectum by the inferior mesenteric artery.
- Origin of the inferior mesenteric artery from the abdominal aorta at the level of the lumbar vertebra.
Note: The inferior mesenteric plexus (inferior mesenteric ganglion) surrounds the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery.
- The left colic artery: supplies the descending colon, an ascending branch anastomoses with the middle colic artery, a descending branch anastomoses with a sigmoid artery.
- Sigmoid arteries: 2-4 arteries, several small branches to the sigmoid colon, anastomoses with the left colic artery and superior rectal artery.
- The superior rectal artery: runs dorsally to the upper rectum, anastomoses with the sigmoid artery and the middle rectal artery from the internal iliac artery.
- Left colonic flexure: watershed between the supply area of the superior mesenteric artery and the inferior mesenteric artery.
- Anastomosis between the superior mesenteric artery (middle colic artery) and the inferior mesenteric artery (left colic artery) near the left colonic flexure distally (Riolan's anastomosis).
Note: Inconsistant: Riolan's anastomosis is not or not sufficiently developed in 20% of cases.
- Drummond's arcade: vascular arcade that connects the branches of the colic branches of the superior mesenteric artery and the inferior mesenteric artery near the intestine and runs caudally near the colon.
- Venous drainage via the left colic vein and sigmoid veins into the inferior mesenteric vein, which drains into the splenic vein behind the pancreatic tail. This forms the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein and other visceral veins behind the pancreatic head.
- Lymphatic drainage along the inferior mesenteric artery (left colic lymph nodes, sigmoid lymph nodes).
- Important neural structures:
- Inferior mesenteric plexus (inferior mesenteric ganglion) (autonomic nervous system) at the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery.
- Involved sympathetic nerves: lumbar splanchnic nerves, involved parasympathetic nerves: pelvic splanchnic nerves via the inferior hypogastric plexus.