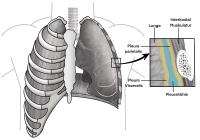
- The Pleura
The thoracic cavity is an enclosed serous space lined by the pleura. The pleura divides at its reflection at the lung hilum and the pulmonary ligament into the visceral and parietal layers. The narrow space between the pleural layers is filled with a small amount of serous fluid and serves as a sliding and adhesion layer for the lung.
Pleurodesis refers to the obliteration of this space and adhesions of the pleural layers through chemically or thermally induced damage followed by a local inflammatory reaction or through surgical removal of the parietal pleura.
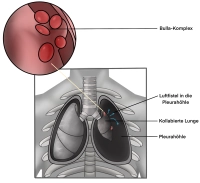
- Bullae and Blebs
Blebs or bullae refer to small air-filled cavities or enlarged alveoli. These are usually found subpleurally and at the lung apex or in the apical area of segment 6. In addition to the typically large and ubiquitously occurring bullae and lung structural changes in chronic lung diseases, these blisters can also occur in young, lung-healthy patients and lead to pneumothorax.