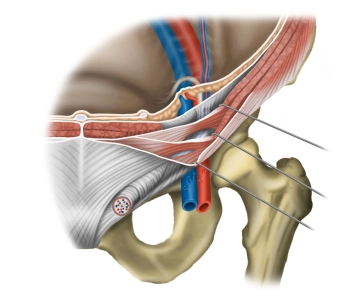
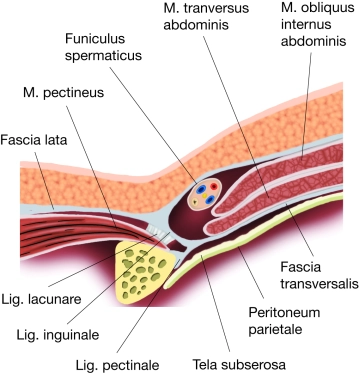
The inguinal region (transition between the anterior abdominal wall and lower extremity) has several weak points through which a hernial sac with or without contents can protrude through the abdominal wall (women more femoral hernias, men more inguinal hernias). As the area below the inguinal ligament, the inguinal canal is divided into two compartments by a division of the inguinal ligament (arcus iliopectineus): the lacuna vasorum and the lacuna musculorum.
Lacuna vasorum
- Located next to the pubic bone, it serves as the passageway for the external iliac artery and vein (→ femoral artery and vein, arrangement: artery lateral to the vein). Additionally, the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve passes through it laterally, and the deep inguinal lymph nodes (Rosenmüller) are found caudally medially within it. The lacuna vasorum represents the internal hernial gap for femoral hernias (through the femoral septum next to the femoral vein).
Lacuna musculorum
- Located lateral to the lacuna vasorum, it serves as the passageway for the psoas major muscle and iliacus muscle (together = iliopsoas muscle), as well as the femoral nerve and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (cranially).