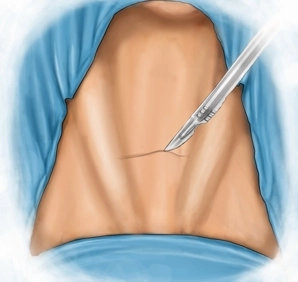
Transverse skin incision, about 3 cm, long, inferior to the thyroid cartilage and about 1-2 finger widths superior to the jugular fossa. Take down the skin and platysma to the superficial cervical fascia.
-
Skin incision
-
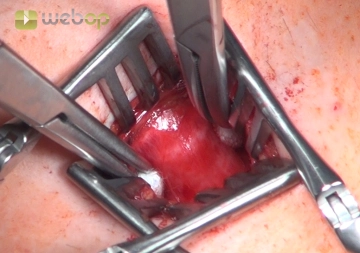
Tracheal access
After transverse transection of the superficial cervical fascia incise the pretracheal lamina in the midline and dissect down. After splitting the strap muscles expose the anterior tracheal wall at the level of the 3rd and 4th cartilage ring with two retractors; the thyroid isthmus may have to be pulled craniad.
Note: Excise the thyroid isthmus if it continues to block the anterior tracheal wall, and suture-ligate its transection margins to both lobes of the thyroid.
-
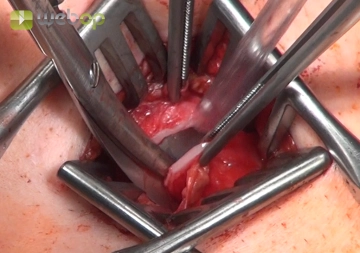
Tracheal fenestration
If possible, fenestrate the trachea between the second and third cartilage ring. In doing so, incise the annular ligament of the trachea the full width of the anterior tracheal wall. At both sides of the tracheal wall, cut through the second and third cartilage ring and the annular tracheal ligament with scissors. This creates a fenestration with inferior base.
Note: Before incising the trachea, it must be verified that the cuff of the translaryngeal tube is outside the surgical field. If this is not the case, the tube should be advanced further, thereby protecting the cuff from damage.
-
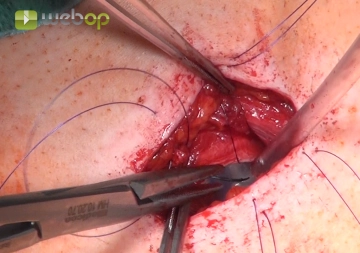
Transcutaneous fixation of the fenestration
After careful hemostasis, the tracheostomy is epithelialized by suturing the skin to the margin of the tracheal fenestration. First, suture the skin in the inferior part of the wound to the folded-back fenestration and then suture the mobilized margin of the skin to the trachea (in both cases interrupted horizontal mattress sutures 4/0, monofilament, delayed absorption).
-
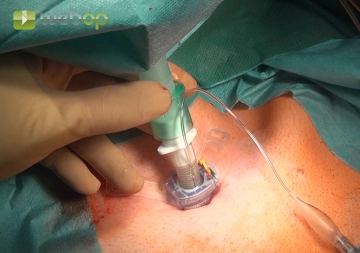
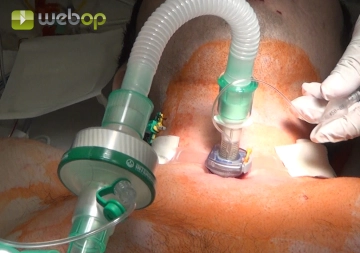
Inserting and connecting the tracheostomy tube
-
Outer fixation