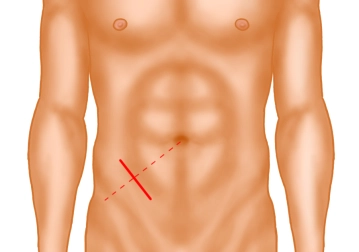
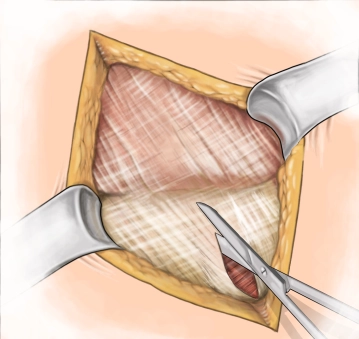
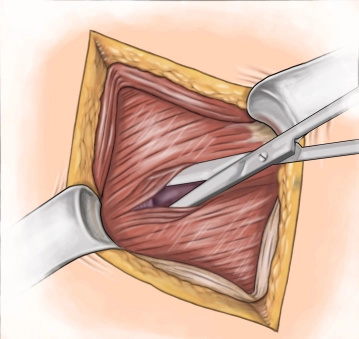
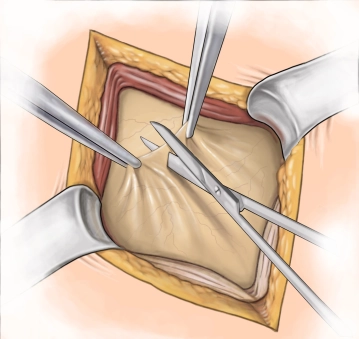
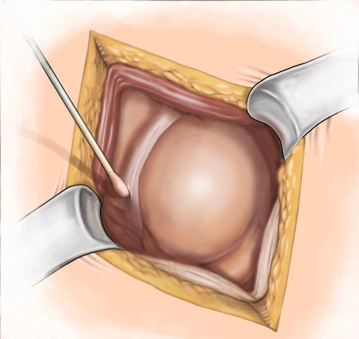
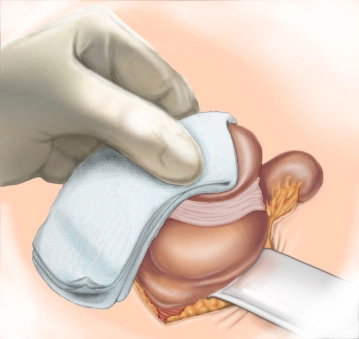
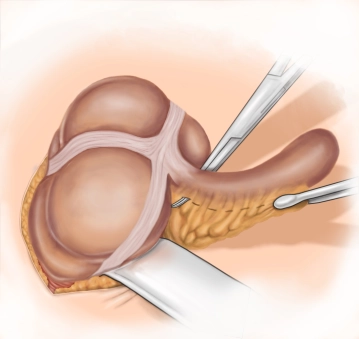
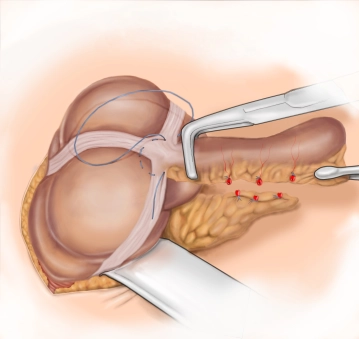
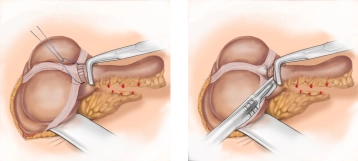
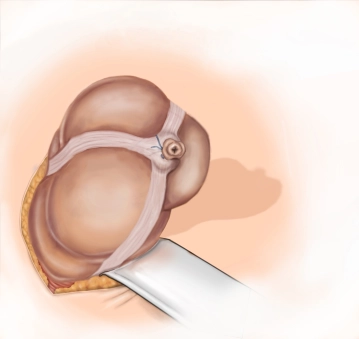
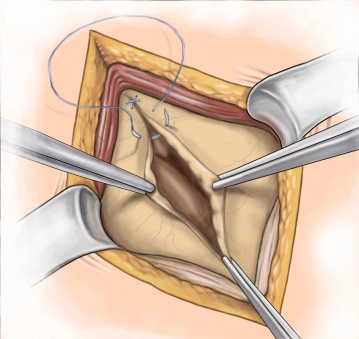
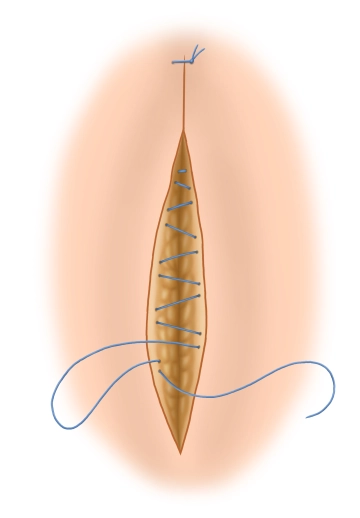
A transverse incision approximately 3-4 cm long is made in the right lower abdomen (on an imaginary line between the anterior superior iliac spine and the navel in the caudal third). Subsequently, the subcutis and Scarpa's fascia are incised with the electric knife.
Note: The transverse incision should be the standard approach, as the "curtain phenomenon" of the abdominal wall practically prevents incisional hernias, unlike the pararectal incision. The often-cited criticism that a transverse incision cannot be extended if the surgical approach changes is incorrect: The transverse incision can be easily extended cranially as a "hockey stick incision" or medially as a modified "Pfannenstiel incision".