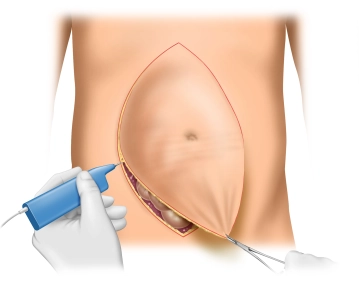
Before the skin incision, the landmarks are marked with a skin marker. These are:
- Costal arch
- Symphysis
- Hernia gap
- if applicable, incision line
Before the skin incision, the landmarks are marked with a skin marker. These are:
Generous wedge-shaped excision of the scar with significantly excess skin from the xiphoid to the symphysis, with the abdominal cavity being opened. Concurrently, adhesiolysis of adherent intestinal loops is performed.
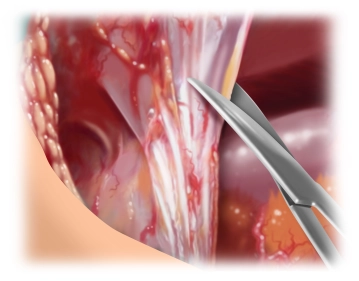
Systematic adhesiolysis along the abdominal wall laterally up to the level of the anterior axillary line to avoid unnoticed bowel injury during interparietal preparation of the abdominal wall layers.
If there is no history of passage problems or recurrent ileus conditions, interenteric adhesiolysis can be omitted.
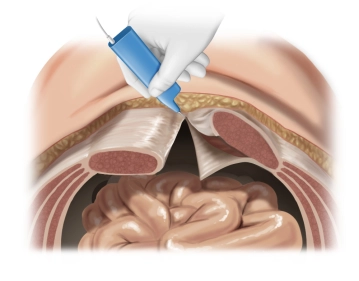
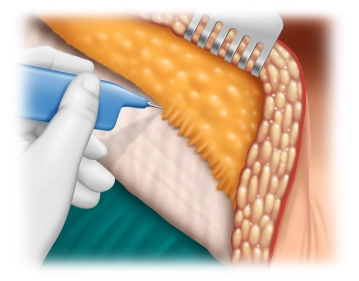
The posterior rectus sheath is visualized and incised longitudinally as close as possible to the medial edge. Then, preparation of the retro-muscular space by bluntly detaching the rectus muscles from the posterior layers of the rectus sheath. Laterally, the preparation is continued until the neurovascular bundles are reached. These must be preserved at all costs and represent the lateral boundary of the preparation.
This preparation extends from retroxiphoid to retropubic into the space of Retzius.
Note:
Below the arcuate line, the extraperitoneal space can be bluntly opened up to behind the symphysis.
Cranially, sharp detachment of the posterior layer of the rectus sheath from the xiphoid by transverse incision on both sides of the linea alba over a length of approximately 5 cm. This allows access to the preperitoneal space. The preperitoneal fat tissue appears as the so-called "fatty triangle." See also our contribution to Incisional hernia surgery with open, retromuscular mesh augmentation
Detachment of the subcutaneous tissue from the anterior rectus sheath laterally to reach the myofascial transition of the external oblique muscle.
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.34/ yearly payment
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$174.70 / yearly payment