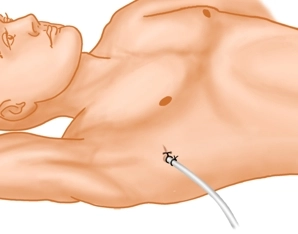
Note: For teaching purposes, the video was recorded with the patient in the lateral recumbent position.
Make a 1- to 2 cm skin incision directly at the level of the rib - in the “safe triangle” between the lower aspect of the pectoralis major muscle, the anterior aspect of the latissimus dorsi muscle, and the mammillary line.
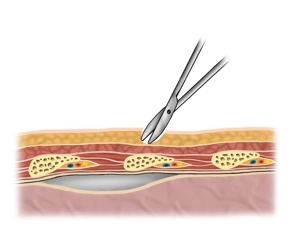
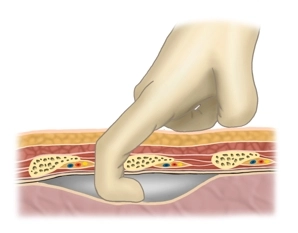
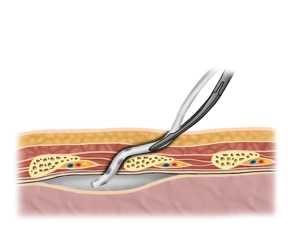
Tip: To avoid subcutaneous emphysema, make the skin incision just wide enough for the index finger which then can bluntly dissect the tissue and guide the tube into place.