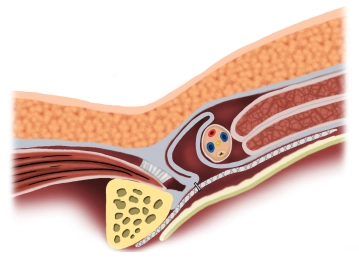
Reinforcement of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal by laparoscopic insertion of a synthetic or biological mesh placed preperitoneally.
-
Principle
![Principle]()
-
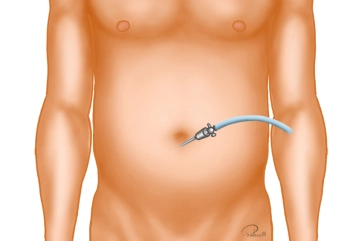
Creation of Pneumoperitoneum
Trocar positioning
The optical trocar (10 mm) is introduced bluntly with scissors after entering the abdomen and the a
The optical trocar (10 mm) is introduced bluntly with scissors after entering the abdomen and the a
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
US$9.40
inclusive VAT
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
from US$7.29 / module
US$87.56/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$14.59
/ month
US$175.10 / yearly payment